IT'S TIME TO LEARN THE DOM 😆
First thing first----> What is the DOM?
DOM stands for Document Object Model. It is the browser's representation of the page in memory. The browser creates the DOM to allow us to modify and change XML, HTML, and CSS. If you change the DOM, you change the page (using JavaScript).
WHY would we want to work in the DOM?
It is a useful tool for developers because it allows a website to be manipulated in a live environment. Once changes made are acceptable and approved, that code that was implemented in the DOM can then be copied over to the actual XML/HTML index file. It can then be saved and implemented so that the website will have the current changes for all end users.
How do we access the DOM and how does it work?
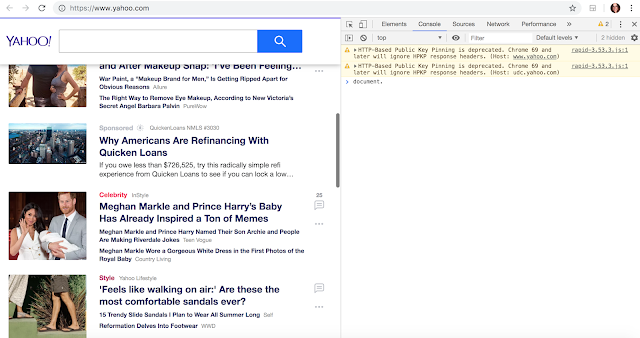
Whenever a webpage is loaded, the browser automatically creates the DOM for that page. To access the DOM, you can right click on the page you are viewing. Select "Inspect", then select "Console". Type "document." then press return. Now you will see the DOM.

Comments
Post a Comment